更多操作
定义
把研究的对象集在一起构成集合。
集合中
有有限个元素:有限集
有无限个元素:无限集
空集
不含元素的集合:[math]\displaystyle{ \emptyset }[/math]
空集也是有限集。
元素和集合的关系
属于:[math]\displaystyle{ \in }[/math]
不属于:[math]\displaystyle{ \notin }[/math]
集合中元素的三个特征
- 确定性:给定的集合,它的元素必须是确定的. 也就是说,给定一个集合,那么任何一个元素是否存在这一个集合中就确定了.
- 互异型:一个给定集合中的元素是互不相同的. 也就是说,集合中的元素是不重复出现的.
- 无序性:给定集合中的元素是不分先后的,没有顺序的.
数集
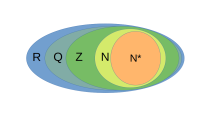
数学里最常用的集合是各种数的集合,简称数集。
示例
- 所有正整数组成的集合称为正整数集,记作 [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{N}^* }[/math],[math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{Z}^+ }[/math] 或 [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{N}^+ }[/math]
- 所有负整数组成的集合称为负整数集,记作 [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{Z}_- }[/math]
- 全体自然数组成的集合称为自然数集,记作 [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{N} }[/math]
- 全体整数组成的集合称为整数集,记作 [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{Z} }[/math]
- 全体有理数组成的集合称为有理数集,记作 [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{Q} }[/math]
- 全体实数组成的集合称为实数集,记作 [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{R} }[/math]
集合的表示方法
列举法
把集合中的所有元素一一列举出来,并用花括号“[math]\displaystyle{ \{ \} }[/math]”括起来表示集合的方法叫做列举法.
注意事项:
- 元素与元素之间必须用“[math]\displaystyle{ , }[/math]”隔开.
- 集合中的元素可以是任何事物.
- 集合中的元素不能重复.
示例:
一元二次方程 [math]\displaystyle{ 3x^2 - 6x = 0 }[/math] 的解集为:[math]\displaystyle{ \{0, 2\} }[/math].
描述法
一般地,设 A 表示一个集合,把集合 A 中所有具有共同特征 P(x) 的元素 x 所组成的集合表示为 [math]\displaystyle{ \{x \in A | P(x)\} }[/math],这种表示方法称为描述法.
注意事项:
- 写清楚集合中元素的符号. 如数或点等.
- 不能出现未被说明的字母.
示例:
奇数集:[math]\displaystyle{ \{x | x = 2n + 1, n \in \mathbb{N}\} }[/math].
偶数集:[math]\displaystyle{ \{x | x = 2n, n \in \mathbb{N}\} }[/math].
子集
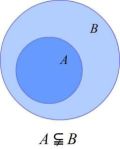
如果集合 [math]\displaystyle{ A }[/math] 的每一个元素都是集合 [math]\displaystyle{ B }[/math] 的元素,就称 [math]\displaystyle{ A }[/math] 是 [math]\displaystyle{ B }[/math] 的一个子集.
记作 [math]\displaystyle{ A \subseteq B }[/math](读作:A 包含于 B)或 [math]\displaystyle{ B \supseteq A }[/math](B 包含 A).
如果 [math]\displaystyle{ A \subseteq B }[/math] 并且 [math]\displaystyle{ B \subseteq A }[/math],就说这两个集合相等,记作:[math]\displaystyle{ A = B }[/math].
如果 [math]\displaystyle{ A \subseteq B }[/math] 但是 [math]\displaystyle{ A \neq B }[/math],就说 A 是 B 的真子集,记作:[math]\displaystyle{ A \subsetneqq B }[/math],读作:A 真包含于 B. 例如,[math]\displaystyle{ (1, 6) \subsetneqq [1, 6] }[/math].
包含关系还有传递性:
- 若 [math]\displaystyle{ A \subseteq B }[/math],[math]\displaystyle{ B \subseteq C }[/math],则 [math]\displaystyle{ A \subseteq C }[/math];
- 若 [math]\displaystyle{ A \subsetneqq B }[/math],[math]\displaystyle{ B \subseteq C }[/math],则 [math]\displaystyle{ A \subseteq C }[/math];
等等.
有限集的子集个数的确定方法
- 含有 [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] 个元素的集合有 [math]\displaystyle{ 2^n }[/math] 个子集;
- 含有 [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] 个元素的集合有 [math]\displaystyle{ (2^n-1) }[/math] 个真子集;
- 含有 [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] 个元素的集合有 [math]\displaystyle{ (2^n-1) }[/math] 个非空子集;
- 含有 [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] 个元素的集合有 [math]\displaystyle{ (2^n-2) }[/math] 个非空真子集.
补集
[math]\displaystyle{ \complement_U A }[/math]
